Looking For A Standalone Spectrum Analyzer For Mac
PhotoPad is designed to be ready to open and edit your photos quickly. Whether you’re a professional photographer or just want to edit your personal photos, PhotoPad offers the powerful tools and features you need to improve your digital images. Photopad professional for mac. * PhotoPad can be added to your right click menu for easy access. About NCH Software: NCH Software offers more than 80 easy-to-use software applications for audio, video, business, dictation and other software utilities for Windows, Mac and mobile devices. PhotoPad Pro Edition for Mac OS X. Retouch photos quickly and easily and edit and apply effects to photos and other images. Crop, rotate, resize and add effects like sepia tones, greyscale, and red eye reduction as well as adjusting the hue, saturation, brightness, contrast and more. PhotoPad Pro Edition for Mac OS X. Retouch photos quickly and easily and edit and apply effects to photos and other images. Crop, rotate, resize and add effects like sepia tones, greyscale,.
- Looking For A Standalone Spectrum Analyzer For Mac
- Looking For A Standalone Spectrum Analyzer For Macbook Pro
What Is WiFi Spectrum Analysis? A WiFi spectrum analysis is the process of measuring the WiFi signal in a certain area and determining its strength.
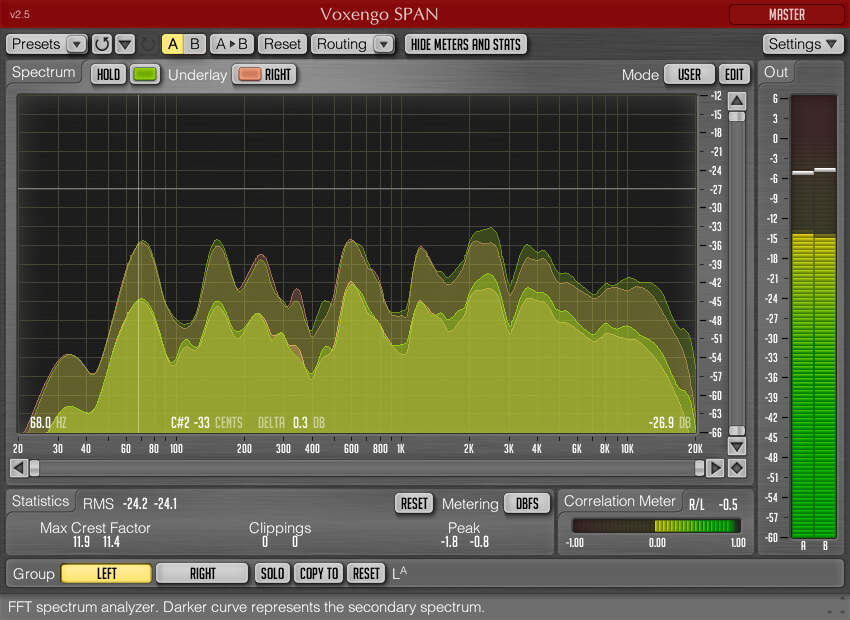
A WiFi spectrum analysis is typically performed to find interference that negatively impacts wireless performance and to eliminate it. WiFi networks are broadcasted either on the 2.4 or the 5 GHz frequency band. Each of these two frequency bands is divided into multiple channels, which provide a degree of separation of individual networks. Ideally, no two WiFi networks should run on the same channel, but this is seldom possible in practice. Because of the steep rise of mobile and IoT (Internet of Things), the WiFi frequency spectrum has never been more crowded. But it’s not just WiFi networks themselves that cause interference and corrupt other WiFi signals, most common electronic devices can create interference and noise as well.
That includes microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, car alarms, CCTV wireless surveillance video cameras, and cordless phones. Without WiFi spectrum analyzers, locating the exact source of interference would be unreasonably difficult. Fortunately, there are many excellent WiFi spectrum analyzer software solutions available today, and many of them, including NetSpot, are so easy to use that even home users without any IT training can use them to optimize their home networks and say goodbye to slowdowns and connection drops. When Should I Perform a Spectral Analysis? A WiFi spectral analysis should be performed throughout the lifecycle of a WiFi network.
First, it’s necessary to analyze the area of deployment to determine whether there is some kind of existing interference. In most cases, there will be other WiFi networks, and sometimes even Bluetooth devices or large electric appliances. After the most optimal WiFi frequency band and channel are selected and the network is deployed, an ongoing spectrum analysis should iron out all performance problems and look for new sources of interference. While this process may sound complicated and time-consuming on paper, modern wireless spectrum analyzers such as NetSpot make it completely painless and extremely fast. In the next section of this article, we explain how to select a wireless spectrum analyzer and introduce NetSpot as the best wireless spectrum analyzer for macOS and Windows.
Which WiFi Spectrum Analyzer Should I Use? A good WiFi spectrum analyzer should meet certain criteria. It should be able to pick up all signals on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies and identify all 802.11 networks. 802.11 technology is a set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications for implementing wireless local area networks, and there are several different 802.11 protocols used by modern wireless routers and devices today. The following three are by far the most common:. 802.11g: has a throughput of 54 Mbit/s using the 2.4 GHz band.
802.11g hardware is fully backward compatible with the previous 802.11 specification, 802.11b. 802.11g suffers from the same interference as 802.11b in the already crowded 2.4 GHz range. 802.11n: has a throughput of 600 Mbit/s using either the 2.4 or 5 GHz frequency band.
Looking For A Standalone Spectrum Analyzer For Mac
802.11n uses a wireless-networking standard that uses multiple antennas to increase data rates, MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output). 802.11n doubles the channel width, from 20 MHz to 40 MHz, which results in slightly more than double the data rate over the congested 2.4 GHz band. 802.11ac: developed from 2008 through 2013 and published in December 2013 in the IEEE Standards Association, 802.11ac has a multi-station throughput of at least 1 Gbit/s and single-link throughput of at least 500 Mbit/s. It extends the channel with to 160 MHz and adds more MIMO spatial streams (up to eight) and downlink multi-user MIMO (up to four clients). Besides latest 802.11 protocols, a good RF spectrum analyzer should also be able to check security settings and understand the three most commonly used WiFi security protocols, which are WEP, WPA, and WPA2. WEP: ratified in 1997, WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a security algorithm for IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. In 2004, WEP was declared deprecated by the IEEE due to its weak security.

Looking For A Standalone Spectrum Analyzer For Macbook Pro
While there are still many networks that WEP, the security they provide couldn’t hold up to any serious hacking attempts. WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access is a security protocol and security certification program developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance as a replacement for WEP. Available since 2003, WPA includes a Message Integrity Check, which is designed to prevent an attacker from altering and resending data packets, replacing the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) that was used by the WEP standard. WPA2: while not perfect, WPA2 is the most commonly used WiFi security protocol and security certification program today, and it includes an AES-based encryption mode as well as support for CCMP (Counter Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol). In January 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced WPA3 as a replacement to WPA2, but it will still take some time before WiFi routers and devices will support it. NetSpot not only supports the full breadth of 802.11 protocols and WiFi security protocols but it also is able to generate a comprehensive visual survey of WiFi signal, clearly highlighting all areas of signal weakness. For quick assessments, NetSpot offers the so-called Discover mode, which instantly collects every detail about surrounding WiFi networks and presents the gathered information as an interactive table.





